AI
"AI is Confusing — Here’s Your Cheat Sheet"
23 July 2024
|
Zaker Adham
If you find yourself lost in the maze of AI jargon, you're not alone! Artificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing the tech world, with companies across the globe touting their latest advancements. However, understanding the plethora of terms used in the AI landscape can be quite challenging. To help you make sense of it all, we've compiled a cheat sheet of essential AI terms, explaining what they mean and why they matter.

What Exactly is AI?
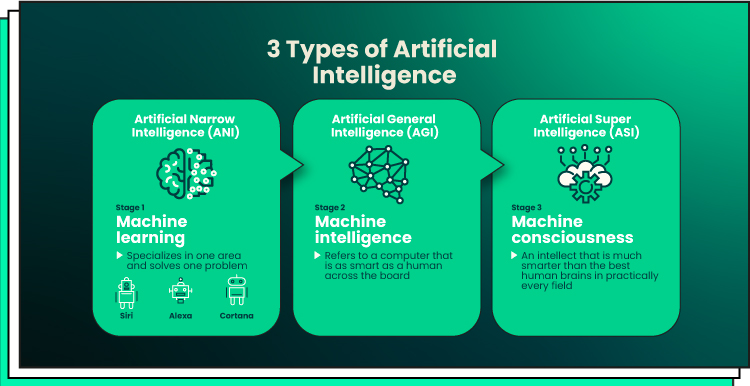
Artificial intelligence (AI): AI is the branch of computer science aimed at creating systems capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence. Today, AI is a buzzword used to describe technologies that mimic human thought processes.

For example, Google leverages AI to enhance its products and services, while companies like OpenAI and Meta develop AI models like GPT and chatbots.
Common AI Terms You Should Know
Machine Learning: This subset of AI involves training computer systems on data to enable them to make predictions or decisions without explicit programming. Machine learning powers many AI applications, allowing systems to "learn" from data.
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI): AGI refers to AI systems that possess human-like intelligence. While AGI holds immense potential, it also raises concerns about superintelligent machines.
Generative AI: This technology can create new content such as text, images, and code. Popular examples include ChatGPT and Google's Gemini, which generate responses and images based on their training data.

Hallucinations: In the AI context, hallucinations refer to instances where generative AI tools produce inaccurate or nonsensical results due to limitations in their training data.
Bias: AI systems can exhibit biases based on the data they are trained on. For instance, facial recognition software might struggle with accuracy across different demographics, highlighting the importance of diverse training data.
Understanding AI Models
AI Model: An AI model is trained on data to perform tasks independently. For example, large language models (LLMs) like OpenAI's GPT can process and generate human-like text.
Large Language Models (LLMs): These AI models handle natural language processing, enabling them to understand and generate text. LLMs like Claude by Anthropic are designed to interact conversationally.
Diffusion Models: Used to generate images from text prompts, diffusion models learn by adding and then removing noise from images. They are also used in audio and video generation.
Foundation Models: These versatile generative AI models are trained on extensive datasets and can be adapted for various tasks without additional specific training.
Additional AI Concepts
Training: Training involves feeding AI models vast amounts of data to help them recognize patterns and make predictions. This process requires significant computing power and resources.
Parameters: Parameters are variables within an AI model that determine its output based on input data. The more parameters, the more complex and sophisticated the model.
Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP enables machines to understand and generate human language, as seen in applications like ChatGPT and OpenAI's Whisper speech recognition.
Inference: Inference is the process by which AI applications generate responses or perform tasks based on their training. For example, when ChatGPT provides a recipe, it is performing inference.
Neural Network: This computer architecture uses interconnected nodes to process data, akin to the human brain's neurons, enabling AI systems to learn and recognize patterns.
Transformer: A type of neural network that processes sequences of data by understanding the relationships between elements. Transformers are fundamental to the development of generative AI technologies.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG): RAG allows AI models to access external data during generation, enhancing accuracy and reducing hallucinations.
AI Hardware
Nvidia’s H100 Chip: This popular GPU is essential for AI training, handling complex AI workloads efficiently. Demand for such chips has skyrocketed, driving innovations in AI hardware.
Neural Processing Units (NPUs): NPUs are specialized processors in devices that handle AI tasks more efficiently than traditional CPUs or GPUs, enabling features like real-time video call enhancements.
TOPS: This term, meaning "trillion operations per second," is used by tech vendors to highlight the processing power of their AI hardware.
Leading AI Companies and Tools
OpenAI / ChatGPT: OpenAI's ChatGPT has made AI mainstream, sparking widespread interest and competition among tech giants.
Microsoft / Copilot: Microsoft's Copilot integrates AI into various products, leveraging OpenAI's models.
Google / Gemini: Google is rapidly advancing its AI capabilities with the Gemini suite of tools.
Meta / Llama: Meta focuses on its Llama model, offering an open-source alternative to proprietary AI systems.
Apple / Apple Intelligence: Apple is enhancing its products with AI under the Apple Intelligence banner, including integrating ChatGPT with Siri.
Anthropic / Claude: Anthropic, backed by major investments, develops the Claude AI models, aiming to push the boundaries of AI technology.
xAI / Grok: Elon Musk's xAI is making waves with its Grok LLM, backed by substantial funding.
Perplexity: Known for its AI-powered search engine, Perplexity is making significant strides in AI technology.
Hugging Face: This platform serves as a hub for AI models and datasets, facilitating collaboration and innovation in the AI community.
By familiarizing yourself with these terms, you'll be better equipped to navigate the rapidly evolving world of AI. Whether you're a tech enthusiast or a professional, understanding these concepts is crucial as AI continues to shape the future.